Blog
Harnessing Uncertainty: The Power of Risk Management In Driving Project Outcomes

In the fast-paced world of project management, uncertainty can often be the only guarantee. With complexities and change constants in any venture, the ability to adeptly manage risk is not just a skill but an indispensable part of ensuring project success.
Managing risks effectively means steering your project clear of uncharted dangers while capitalizing on unexpected opportunities. It’s an unpredictable strategic dance that requires finesse and knowledge-driven choreography to maintain balance.
This article delves into how embracing risk management can empower decision-makers, bolstering their capability to drive projects toward their intended outcomes, even amidst tempestuous scenarios.
Read on to discover how mastering this art form of control can unlock profound value for your endeavors.
Key Takeaways
- Risk management in project management involves a strategic approach that identifies, evaluates, and controls potential risks to enhance decision-making and secure successful outcomes.
- A structured risk management process consists of six key steps: developing a plan, identifying risks, conducting qualitative and quantitative analyses, evaluating the severity of each risk, planning responses, and continuously monitoring all identified risks throughout the project lifecycle.
- Utilizing specialized tools like risk registers, SWOT analysis, enterprise risk management software and predictive analytics helps manage risks more effectively by providing structured documentation and real-time data insights for informed decisions.
- Project managers can mitigate negative impacts on projects by employing advanced methods such as statistical models for quantitative analysis and robust frameworks supported by technology to optimize positive opportunities.
What is Risk Management in Project Management?
Definition and purpose
Risk management in project management is the strategic approach to dealing with potential pitfalls that could jeopardize a project’s objectives. It involves steps that help identify, evaluate, and prioritize risks, followed by coordinating an economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events.
This proficiency allows for capitalizing on opportunities when they arise. The main purpose is to prevent losses and ensure that any risk taken aligns well with long-term goals, thereby ensuring successful project outcomes.
Risk managers create value through careful assessment and planning using this structured process to tackle uncertainties head-on. They make decisions more confidently, translating into stronger governance practices within their projects.
Navigating through complexities becomes more manageable when one anticipates scenarios through a detailed risk-analysis framework—a critical tool in driving decision-making processes forward toward achieving project deliverables efficiently.
Importance of risk management in project management
Risk management is a crucial process in any project, regardless of its size or complexity. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could impact the project’s success. By proactively managing risks, project managers can increase their chances of delivering the project on time, within budget, and to the required quality.
- Preventing Cost Overruns: One of the significant benefits of project risk analysis is its role in preventing cost overruns. Project managers can allocate resources more effectively and avoid financial pitfalls by identifying potential risks that could impact the budget early on.
- Ensuring Timely Delivery: Delays can be detrimental to project success. Project managers can identify potential bottlenecks and challenges that may lead to delays through risk analysis. By addressing these issues proactively, projects are more likely to stay on schedule.
- Enhancing Stakeholder Confidence: Stakeholders, whether internal or external, crave certainty. Providing them with a comprehensive risk analysis demonstrates foresight and a proactive approach. This, in turn, enhances confidence in the project team’s ability to deliver successful outcomes.
The Risk Management Process
Risk management in project management is a structured approach to managing uncertainty. Teams can effectively anticipate and address potential project pitfalls through six clear steps.
- Developing a Risk Management Plan: Craft a strategy that outlines how risks will be identified, analyzed, and managed throughout the project life cycle. This plan becomes a part of your overall project plan, detailing roles, responsibilities, budget for risk management activities, timing for risk management tasks, and risk thresholds.
- Identifying Risks: Start by compiling a comprehensive list of possible risks affecting your project. Use tools like brainstorming sessions, checklists, and past project experiences to uncover financial uncertainties and employee turnover risks. A detailed risk breakdown structure can offer valuable insights at this stage.
- Performing Qualitative Analysis: Evaluate the impact and likelihood of each identified risk using qualitative methods. If they occur, gauge these risks based on their severity and effect on project objectives.
- Performing Quantitative Analysis: Further, analyze risks’ probability and potential impact using numerical values. This helps in understanding the actual exposure of the project to these risks and aids in making informed decisions on which risks need more focus.
- Assessing Risks through Evaluation: Prioritize the identified risks by comparing them against business objectives and thresholds in your policy documents. Employ tools like risk matrices or dashboard visualizations provided by enterprise risk management software to streamline this process.
- Planning Risk Responses: Determine actions for each high-priority risk on your list—whether it’s avoidance, mitigation, transfer (such as outsourcing or insurance), or acceptance—and integrate these responses into your overall project plan.
Tools and Techniques for Risk Management
Risk management in project management involves identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and mitigating potential risks that could impact the success of a project. Here are some common methods used in risk management:

Risk Identification:
- Brainstorming: Gather diverse stakeholders to generate a comprehensive list of potential risks.
- Checklists: Refer to historical data, lessons learned, or industry-specific checklists to identify common risks.
- Team Brainstorming Ideas: Utilize the power of brainstorming, surveys, and focus groups to tap into insights not captured by mere numbers. Engage project team members, stakeholders, customers, and subject matter experts to generate valuable insights for risk identification and response planning.
Risk Assessment:
- Qualitative Risk Analysis: Evaluate risks based on their probability and impact using probability and impact matrix or risk scoring methods.
- Quantitative Risk Analysis: Assign numerical values to risks, often involving statistical models to quantify the potential impact and likelihood.
- Creating the Risk Report: Develop a Risk Report as a summary reflecting risks that have occurred, actions taken, and potential impacts to budget, timeline, and deliverables. Use it as a communication tool for conveying risk status to the team and stakeholders.
Risk Prioritization:
- Risk Prioritization Matrix: Use a matrix to prioritize risks based on their severity, likelihood, and other relevant factors.
- Risk Categorization: Group risks into categories (e.g., technical, organizational, external) to focus on specific areas.
- Examining the Risk Register: Regularly update the Risk Register throughout the project life cycle, documenting each risk, related activities, and status.
Risk Response Planning:
- Avoidance: Take actions to eliminate the risk or change the project plan to avoid the risk altogether.
- Mitigation: Develop strategies to reduce the impact or likelihood of a risk.
- Transfer: Shift the risk to another party, often through insurance or outsourcing.
- Acceptance: Acknowledge the risk and budget for potential impacts without taking specific actions to mitigate.

Monitoring and Control:
- Regular Review: Continuously monitor identified risks and assess their status throughout the project lifecycle.
- Trigger Identification: Establish triggers or indicators that signal when a risk is about to occur or has occurred.
- Contingency Plans: Develop contingency plans for high-priority risks to be implemented if they materialize.

Documentation:
- Risk Register: Maintain a comprehensive log of identified risks, their characteristics, and the planned responses.
- Lessons Learned: Document and analyze risks encountered during the project for future reference.
- Creating a Probability and Impact Risk Matrix: Use a matrix to assess risk probability and impact, determining early in the project and maintaining consistency throughout.

Communication:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Keep stakeholders informed about potential risks, mitigation strategies, and any changes to the risk profile.
- Reporting: Provide regular risk reports to project sponsors, team members, and other relevant parties.
- Scenario Analysis: Conduct “What-If” and Sensitivity Analysis to explore various scenarios and understand potential impacts.
By employing these methods and tools, project managers can proactively identify and address risks, enhancing the likelihood of project success. Remember that risk management is an ongoing process, and adjustments may be needed as the project progresses. Tailoring risk management plans to the project’s needs ensures the effective use of qualitative and quantitative data for increased objectivity and accuracy.
Creating a Risk Management Plan
In establishing a risk management plan, project managers synthesize their expertise to design a bespoke blueprint, pivotal for foreseeing and counteracting potential hazards.
This plan hinges on continuously populating and refining the risk register—essentially a dynamic document chronicling identified risks and corresponding response strategies—thereby ensuring its relevance throughout the project lifecycle.
- Formulate clear objectives aligned with the project scope.
- Define roles and responsibilities for risk management activities.
- Set criteria for assessing risk impact and likelihood.
- Determine thresholds for low, medium, and high risks.
- Develop standardized response actions, including avoidance, reduction, transfer, or acceptance.
Attention to detail in these stages fortifies the foundation of your plan against unforeseen turbulence that could otherwise thwart project milestones.
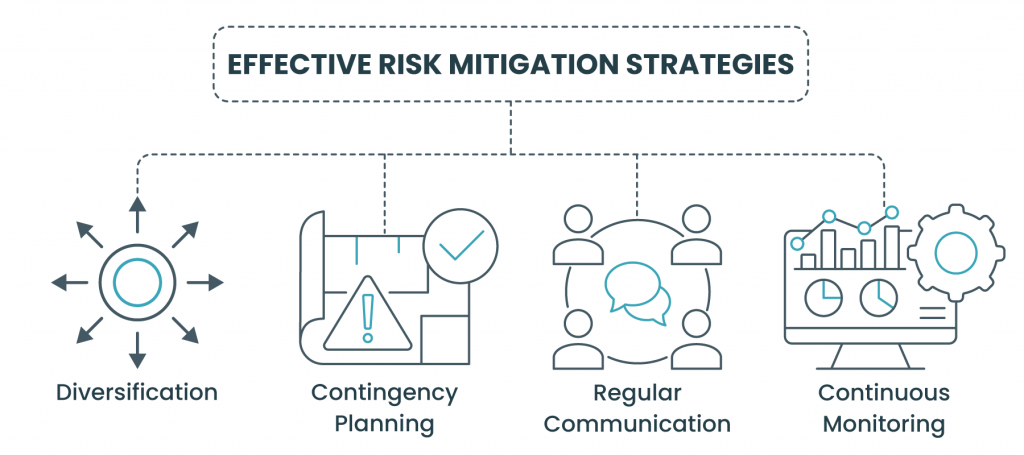
Effective Risk Mitigation Strategies
Mitigating risks is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. The effectiveness of mitigation strategies depends on the nature of the project and the specific risks at hand. Let’s explore some universally effective risk mitigation strategies.
- Diversification: Just as a well-balanced investment portfolio minimizes financial risks, diversifying resources and dependencies minimizes project risks. Avoid over-reliance on a single supplier, technology, or team member.
- Contingency Planning: Develop contingency plans for identified high-impact risks. These plans outline specific actions to be taken if a risk materializes, ensuring that the project can swiftly recover without significant disruptions.
- Regular Communication: Open and transparent communication is a powerful risk mitigation tool. Encourage team members to communicate challenges and roadblocks promptly. This enables quick response and resolution, preventing issues from escalating.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing risk management tools, such as risk assessment software and GRC software, facilitates continuous monitoring of the project landscape. Real-time data allows for agile decision-making and proactive risk management.
Conclusion
Harnessing the power of risk management transforms uncertainty into a roadmap for success. By mastering risk analysis, project managers craft strategies that anticipate potential pitfalls and reveal hidden opportunities.
Considering risks systematically ensures your projects adapt proactively, maintaining their course through storms of uncertainty. The tools and methodologies discussed equip teams to navigate unknowns, confidently turning what-if scenarios into realized achievements.
As we venture forward, embracing dynamic risk management positions us at the forefront of innovation and growth. Let this be the moment you redefine how to lead projects boldly into future horizons.




























 Task Management
Task Management 















 Customization
Customization
