Blog
A Comprehensive Guide to Change Management for Projects
Change is the only constant in the world of project management. In today’s fast-paced business environment, projects constantly evolve, and project managers must adapt to these changes to ensure successful outcomes. This is where change management comes into play. This comprehensive guide will delve into what change management is, its role and benefits, the implementation steps, techniques, best practices, and the future of change management.
What is Change Management in Project Management?
Change management in project management refers to the structured approach and processes used to ensure that changes to a project’s scope, objectives, timeline, or deliverables are effectively managed. It involves preparing and supporting individuals, teams, and organizations to embrace and adapt to changes initiated within a project.
Project managers encounter various changes throughout the project lifecycle, whether it’s a change in project requirements, technology, resources, or market conditions. These changes can lead to confusion, resistance, and project failure without proper change management.
The Role and Benefits of Change Management
Why Change Management Matters in Project Management
Change management is vital in project management for several reasons. Firstly, it helps project managers anticipate and address potential challenges associated with changes. Secondly, it ensures that stakeholders are well-informed and engaged in the change process, reducing resistance, and increasing buy-in. Lastly, effective change management enhances the overall success rate of projects.
Benefits of Implementing Change Management
Implementing change management offers a multitude of benefits, including:
1) Reduced Resistance
One of the primary benefits of change management is reducing resistance to change within an organization. Resistance to change is a natural human reaction. People often feel threatened or uncertain when faced with changes in their work environment. However, change management strategies are designed to address and alleviate this resistance.
- Understanding the Reasons Behind Change: Change management ensures that employees understand the reasons behind the proposed changes. When individuals comprehend the purpose and objectives of the change, they are more likely to embrace it. It transforms resistance into curiosity and a desire to learn.
- Involvement in Decision-Making: Change management encourages employee involvement in the decision-making process. Employees feel valued and empowered when they have a say in the changes that affect them. Their perspectives are considered, making them more willing to support and adapt to the changes.
- Building Trust: Effective change management builds trust between employees and leadership. When employees see that their concerns are acknowledged and addressed, they are more likely to trust the decisions made by the organization’s leaders. Trust is a cornerstone for successful change adoption.
2) Improved Communication
Communication plays a pivotal role in change management. Open and transparent communication ensures that everyone affected by the change is well-informed, reducing confusion and uncertainty.
- Clarity in Messaging: Change management ensures that messages related to the change are clear and consistent. Ambiguity and misinformation can lead to confusion and resistance. Clear communication helps dispel doubts.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Change management ensures that all stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, and customers, are aligned with the project’s goals. When everyone understands the objectives and benefits of the change, they are more likely to support it.
- Timely Updates: Effective change management provides a structured approach to communication. It ensures that updates and information are disseminated promptly, keeping everyone in the loop throughout the change process.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Change management establishes feedback mechanisms, allowing employees to express their concerns and suggestions. This two-way communication fosters a sense of involvement and helps address any issues.
3) Enhanced Productivity
Change management contributes to enhanced productivity within an organization. When employees adapt to changes quickly and effectively, it minimizes disruptions and improves productivity.
- Minimized Downtime: Properly managed change minimizes the downtime associated with adapting to new processes or systems. Employees can transition smoothly, with minimal disruptions to their daily tasks.
- Skill Development: Change management often includes training and education components. As employees acquire new skills and knowledge, they become more efficient, increasing productivity.
- Motivated Workforce: When employees feel engaged in the change process and understand the positive impact of their efforts, they are more motivated to perform well. This motivation can result in higher productivity levels.
- Streamlined Processes: Change management may involve process improvements. Streamlined and optimized processes can increase efficiency and reduce waste, further enhancing productivity.
4) Risk Mitigation
Change within a project can introduce various risks and challenges. Change management helps organizations identify and mitigate these potential risks, reducing the likelihood of project delays or failures.
- Risk Identification: Change management involves thoroughly analyzing the potential risks associated with the change. This proactive approach helps organizations anticipate issues before they escalate.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Once risks are identified, change management strategies are developed to address them. This may involve contingency plans, alternative approaches, or additional resources to mitigate potential setbacks.
- Contingency Planning: Effective change management includes contingency planning for potential issues during the change process. This preparedness ensures that the project can continue despite challenges.
- Adaptive Resourcing: Change management may involve reallocation of resources to address risks. If a particular aspect of the change process encounters difficulties, resources can be redirected to overcome obstacles.
5) Higher ROI
Ultimately, the goal of any project is to achieve its intended objectives efficiently and effectively. Change management significantly increases the likelihood of success, leading to a higher return on investment (ROI).
- Project Success: Change management ensures that the project aligns with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives. It enhances the chances of achieving the desired outcomes and benefits.
- Reduced Project Failures: Projects without proper change management are more prone to failure due to resistance, miscommunication, and inadequate planning. Effective change management reduces the risk of project failure.
- Optimized Resource utilization: Change management helps organizations maximize their resources. Resources are utilized effectively by ensuring that employees are engaged, processes are efficient, and risks are minimized.
- Long-Term Value: The benefits of change management extend beyond the project’s completion. A well-implemented change management process creates a culture of adaptability, ensuring the organization thrives in a dynamic business environment.
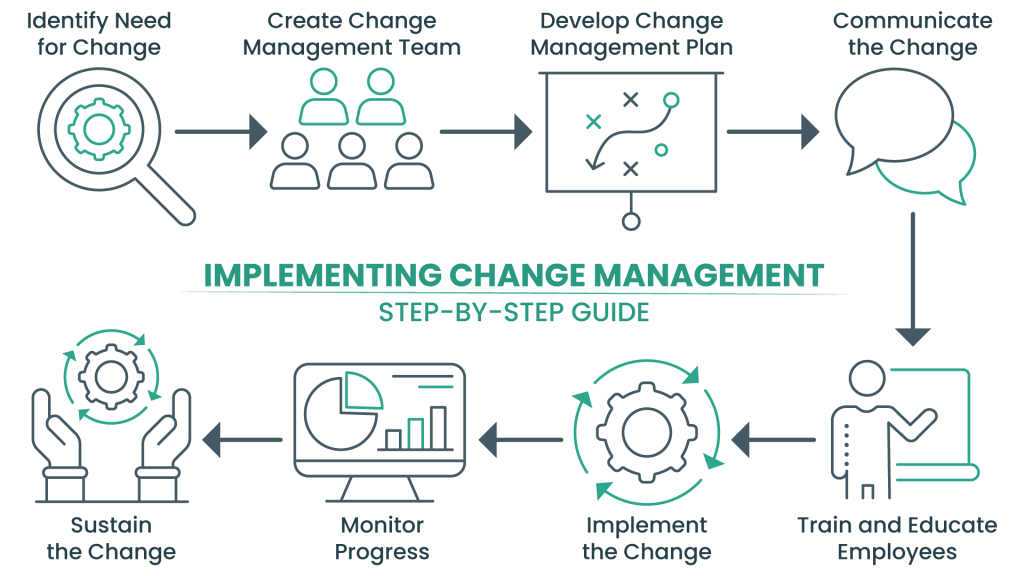
Implementing Change Management: A Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Identifying the Need for Change
The first step in change management is recognizing the need for change. Project managers should assess the current situation, identify pain points, and determine the desired future state.
Step 2: Creating a Change Management Team
A dedicated change management team should be established, consisting of individuals with expertise in change management, communication, and stakeholder engagement.
Step 3: Developing a Change Management Plan
A detailed change management plan should be created, outlining the scope of the change, objectives, timelines, and key stakeholders. This plan serves as a roadmap for the change process.
Step 4: Communicating the Change
Effective communication is crucial. Project managers should communicate the reasons for the change, its impact, and the benefits it will bring. This should be an ongoing process throughout the project.
Step 5: Training and Education
Providing employees with the necessary training and education is essential to ensure they have the skills and knowledge to adapt to the changes.
Step 6: Implementing and Managing the Change
The change is implemented according to the plan, with the change management team monitoring progress and addressing any issues.
Step 7: Monitoring and Measuring Change Progress
Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established to measure the success of the change. Regularly monitoring progress helps identify areas that need adjustment.
Step 8: Sustaining the Change
Once the change is implemented, efforts must be made to sustain it. This involves embedding the change into the organization’s culture and processes.
Techniques for Effective Change Management
Change management can be approached using various techniques and models. Here are some popular ones:
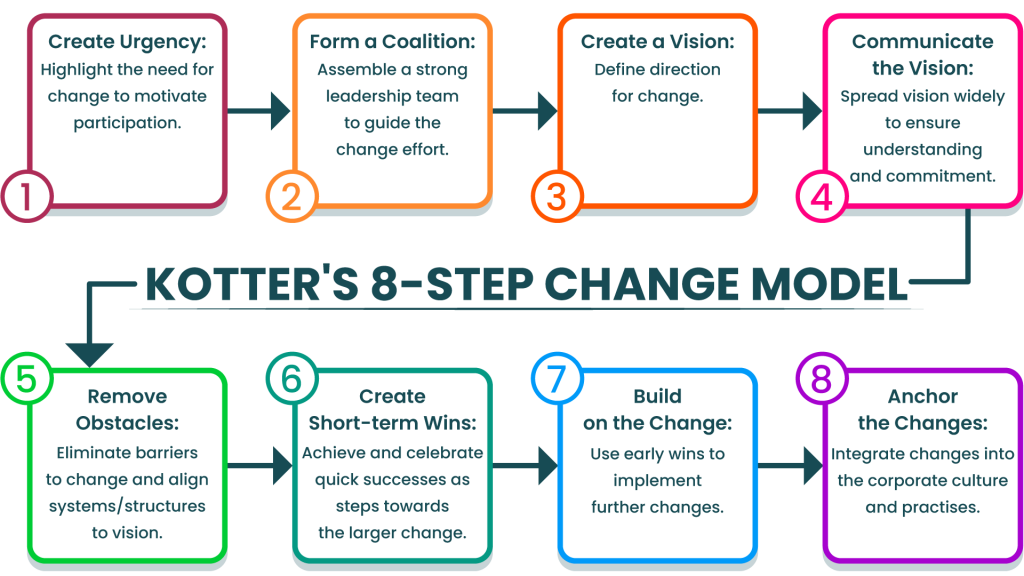
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
This model, developed by John Kotter, provides a structured approach to change management. It includes steps such as creating a sense of urgency, building a guiding coalition, and anchoring changes in the corporate culture.
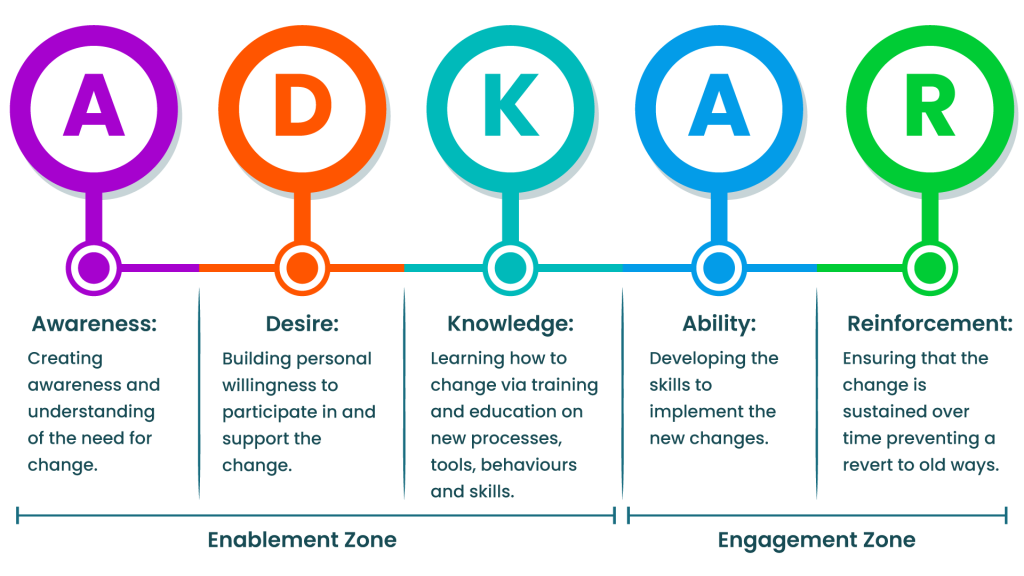
ADKAR Model
The ADKAR model, which stands for Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement, focuses on the individual’s journey through change. It helps identify areas where individuals may struggle and provides targeted interventions.
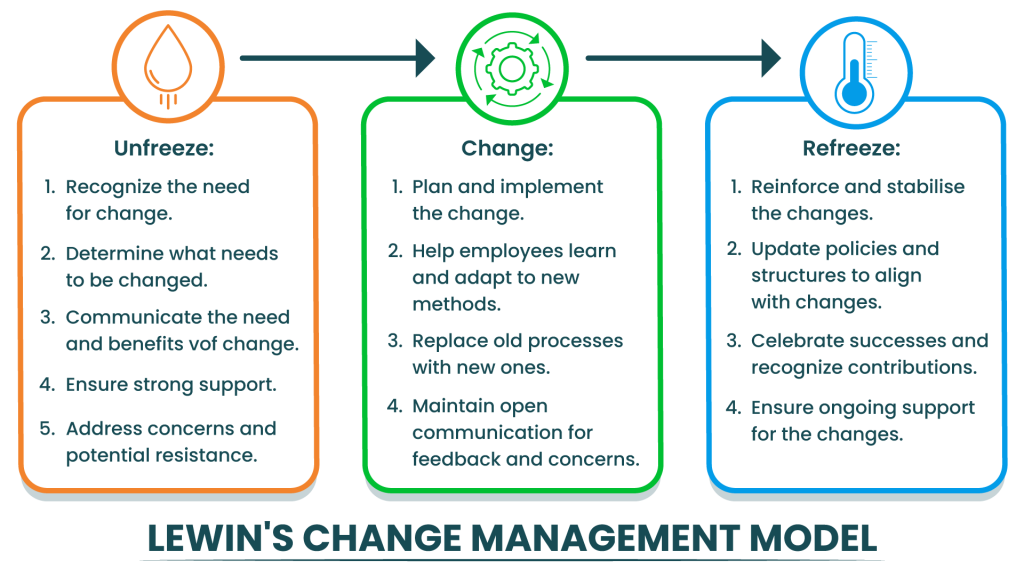
Lewin’s Change Management Model
Kurt Lewin’s model is often represented as a three-step process: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. It emphasizes the importance of preparing people for change, implementing it, and stabilizing it.
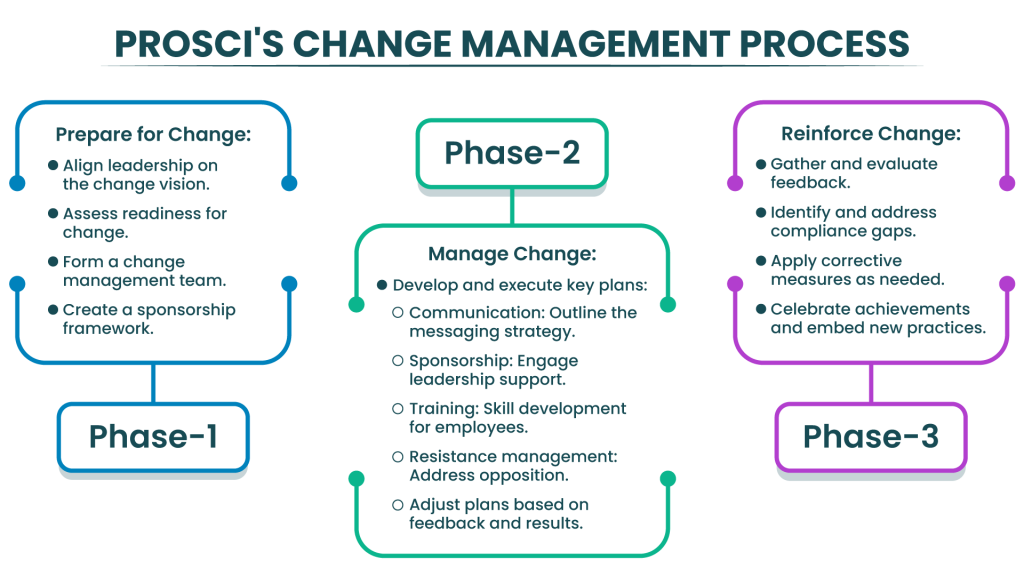
Prosci’s Change Management Process
Prosci’s approach is research-based and includes three phases: preparing for change, managing change, and reinforcing change. It emphasizes the importance of managing the “people” side of change.
Best Practices in Change Management
Engaging Stakeholders
Engaging stakeholders throughout the change process is crucial. This involves involving them in decision-making, soliciting feedback, and addressing their concerns.
Managing Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is natural, but it can be managed. Effective communication, empathy, and involving employees in the change process can help mitigate resistance.
Creating a Culture of Change
Organizations that foster a culture of change are better equipped to adapt to new challenges. Encouraging innovation, learning, and flexibility can contribute to a more adaptable culture.
Leveraging Technology for Change
Technology can be a valuable tool in change management. From communication platforms to project management software, technology can streamline the change process and enhance collaboration.
The Future of Change Management
The Evolution of Change Management
Change management is not static. It has evolved over the years to meet the demands of the ever-changing business landscape. In the future, we can expect to see more agile and data-driven approaches to change management.
Trends Shaping the Future of Change Management
Several trends are shaping the future of change management, including:
- Digital Transformation: The increasing reliance on technology and data is changing how organizations approach change.
- Remote Work: The rise of remote work has necessitated new approaches to change management, as teams are geographically dispersed.
- Agile Methodologies: Agile project management methodologies are becoming more popular, requiring agile change management practices to match.
Conclusion
Change management is a critical component of successful project management. By understanding the role and benefits of change management, following a structured implementation process, utilizing effective techniques, and embracing best practices, project managers can navigate the ever-changing landscape of project requirements and ensure project success. The future of change management promises to be dynamic and responsive to the evolving needs of organizations, making it an essential skill for project managers in the years to come.








































 Task Management
Task Management 


















 Customization
Customization
