Blog
Navigating Complex Projects: The Essential Guide to Critical Path Method
Navigating the labyrinth of project management can be overwhelming, especially when dealing with complex, multi-layered projects. Fortunately, the Critical Path Method (CPM) can be a lifesaver in project management. This technique of critical path analysis not only helps in scheduling and coordinating tasks but significantly enhances efficiency and productivity. Whether you’re an experienced project manager or a novice in the field, understanding the application and benefits of CPM can make a huge difference. This guide will deeply dive into the critical path in project management, how to identify it, and its crucial role in driving project success.
What is the Critical Path in Project Management?
Critical Path: This comprises the uninterrupted series of critical activities within the project schedule, extending from the project’s commencement to its conclusion. The cumulative durations of activities along the Critical Path are equivalent to the overall project duration. Consequently, any delay in the execution of a critical activity will directly translate into a corresponding delay in the project’s ultimate completion date. Therefore, meticulous attention to and management of the Critical Path are imperative to ensure the project stays on schedule.
Understanding the Critical Path Method
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique that uses mathematically based algorithms to determine the longest sequence of tasks required for a project’s completion. It helps create a detailed project schedule, determine task dependencies, and identify the critical path. CPM aims to identify potential delays and bottlenecks in a project, enabling managers to take proactive measures to keep the project on track.
Purpose and Benefits of the Critical Path Method
The primary purpose of CPM is to aid in effective project planning and scheduling. Project managers can prioritize tasks and allocate resources by identifying the critical path. This ensures that the most crucial tasks are completed on time, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns. Additionally, CPM visually represents the project timeline, making communicating with stakeholders and updating them on progress easier.
Benefits of the Critical Path Method
Apart from its purpose in project planning, CPM also offers numerous benefits, such as:
 1. Easy Budget Control:
1. Easy Budget Control:
With a clear path for the project’s on-time completion, you can reduce wasted time and optimize the utilization of your valuable resources. You minimize expensive idle time and ensure efficient resource allocation by reallocating employees from tasks with float time to critical path activities. Additionally, a comprehensive project breakdown aids in optimizing the allocation of other resources, minimizing inventory storage costs.
 2. Effective Scheduling:
2. Effective Scheduling:
The critical path method enables strategic allocation of employees, considering tasks with float time. Employees who are still learning can be assigned tasks with float time, allowing them to focus on skill development. Meanwhile, experienced employees can handle critical path tasks that require immediate attention, ensuring optimal utilization of expertise.
 3. Simplified Project Management:
3. Simplified Project Management:
Rather than comprehending a large, complex project, the critical path method breaks it into manageable tasks. This approach empowers project managers to focus on task-by-task management, facilitating resource management, budget control, and talent utilization as the project progresses.
 4. Efficient Resource Allocation:
4. Efficient Resource Allocation:
The critical path method provides project managers with comprehensive insights into the timing of each activity and the corresponding resource requirements. This knowledge allows for effective resource allocation, ensuring resources are utilized when and where needed. Furthermore, it enables project managers to redirect resources from non-urgent activities to more critical tasks, improving overall efficiency.
 5. Effortless Project Monitoring:
5. Effortless Project Monitoring:
Using the critical path method, project managers can easily break the project into progress chunks using clear charts within project management software. This approach creates a straightforward progress checklist that ensures project managers stay on track. Additionally, the project schedule is effectively divided, allowing project managers to quickly assess if they are on schedule on any given day, ensuring timely project completion.
 6. Straightforward Reporting:
6. Straightforward Reporting:
Project management software offers valuable charts that help project managers identify the critical path of a project. These charts are continuously updated in real-time, enabling project managers to monitor project completion, adherence to schedule, and resource allocation. These real-time reports can be instantly downloaded, providing clear and timely information for effective reporting.
Example of Critical Path Method Process
Let’s delve into the application of the Critical Path Method (CPM) by examining the process of developing and launching a new product. We can gain insights into efficient project management by identifying project tasks, dependencies, and critical paths. In this scenario, we’ll outline various activities involved in the product development and launch and determine the critical path to ensure a timely introduction to the market.
Defining Key Tasks for New Product Development and Launch:
- Initial Market Research and Product Conceptualization
- Design Phase and Creating Prototypes
- Setting Up Manufacturing Processes
- Actual Production of the Product
- Conducting Quality Checks and Testing
- Branding and Packaging
- Establishing Distribution Networks
- Marketing and Advertising Strategies
- Training Sales Teams
- Official Product Launch
Identifying the Critical Path in Product Development:
In new product development, it’s vital to differentiate between tasks that must occur in a specific order (sequential) and those that can happen concurrently. For instance, market research and the initial conceptualization must precede design and prototyping, which in turn must be completed before production. Sequential tasks like these form the project’s critical path and delays in critical path activities directly translate to project delays. An example is the quality assurance phase, which should logically follow production but precede packaging and branding. If quality control is not confirmed prior to branding, it could result in significant issues at launch.
Conversely, some activities, such as sales training or certain marketing efforts, can progress independently of others and can overlap various stages. These tasks do not fall on the critical path and offer more scheduling flexibility.
Understanding and managing the critical path in new product development is key for project managers. It ensures the timely market launch of a product that meets quality expectations and resonates with the target audience, by focusing on sequentially dependent tasks while simultaneously advancing parallel activities.
How To Find the Critical Path in 6 Steps
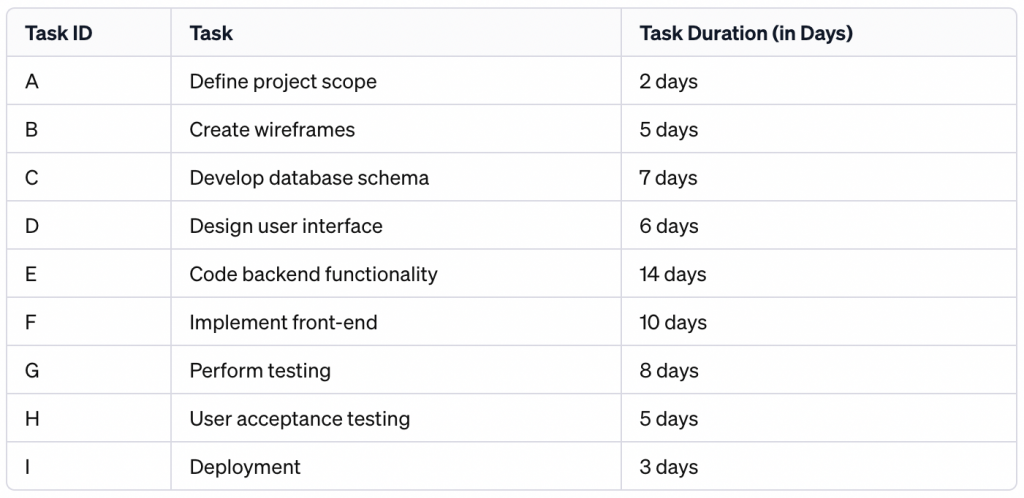
Step 1: Compile Project Activities
Start by making a list of all the tasks you need to complete for your project. Imagine you’re building a software application. Tasks might include defining what the software should do, creating drawings of how it will look, writing the code, and testing it. Assign a time estimate to each task.
Why it’s important: This step helps you have a clear picture of all the work that needs to be done.
Step 2: Identify Activity Dependencies
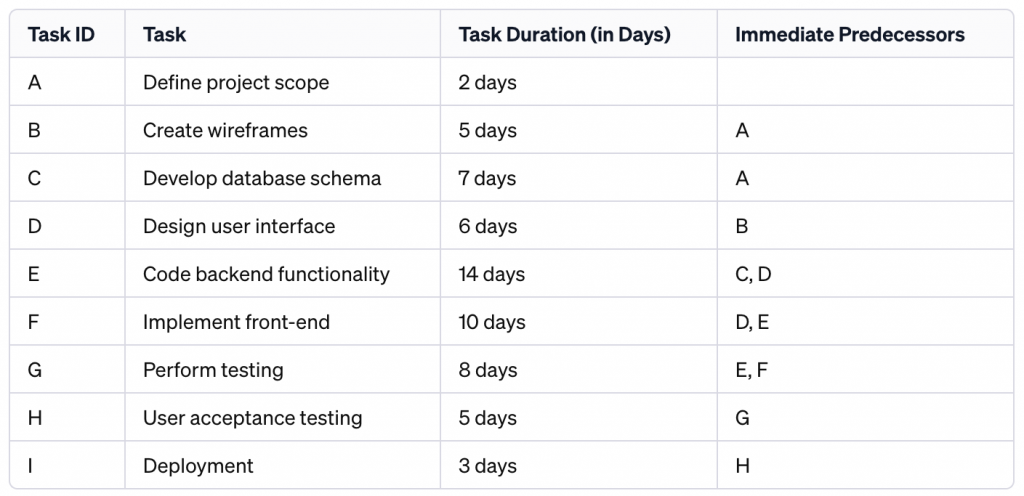
Determine dependencies by specifying which tasks rely on the completion of others. Create an “immediate predecessors” column and list the tasks that must be completed before the current task can start. For instance, you can’t write code until you’ve created a design.
Why it’s important: Understanding these dependencies helps you plan the order in which tasks should be done.
Step 3: Construct a Critical Path Diagram
Create a visual representation of the project with boxes for each task and arrows depicting dependencies using a Gantt chart. Gantt charts are effective tools for illustrating project timelines, task dependencies, and the critical path. Use project management software or specialized tools for Gantt chart creation to visualize the sequential order of tasks and identify those critical to finishing on time.
Why it’s important: Visualizing the project helps you see the order of tasks and which ones are most critical to finishing on time.
Step 4: Calculate Activity Durations
Using the forward pass technique, determine each task’s earliest start and finish dates. This helps establish when each activity should start and finish to meet the project’s deadline.
Why it’s important: Knowing how long each task will take helps you plan when to start and finish each to complete the project on time.
Step 5: Estimate Float Time
Compute the float time for each task using the formula:
Slack time = Late start (LS) – Early Start (ES).
This provides insight into the flexibility of scheduling without impacting project completion.
Why it’s important: Understanding flexibility helps you manage your project timeline effectively.
Step 6: Identify the Critical Path
Isolate tasks with zero float time to identify the critical path. These tasks must be executed precisely on schedule to avoid project delays. Tasks with non-zero float times can be conducted in parallel with critical path activities.
Why it’s important: Knowing the critical path helps you focus on the most important tasks and ensures your project stays on track.
Alternatively, consider using project management software to automate the critical path analysis. Many modern tools are equipped with features that automatically identify dependencies, calculate task durations, estimate float time, and highlight the critical path. This not only adds simplicity to the process but also enhances accuracy by minimizing the risk of manual errors.
CPM vs. PERT: What’s the Difference?
Another term often used when discussing project management techniques is the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT). While PERT and CPM use network diagrams to identify critical paths, the two methods have some key differences.
CPM is ideal for projects with a fixed timeline and well-defined tasks, while PERT is more suitable for projects with uncertain timelines and tasks. Additionally, CPM focuses on identifying the critical path, whereas PERT uses a probabilistic approach to estimate the project’s completion time.
| Basis for Comparison | CPM | PERT |
| What Is It? | A method to control cost and time. | A technique of planning and control of time. |
| Orientation | Activity-oriented | Event-oriented |
| Controls | Control of time and cost | Control of time |
| Estimates | One-time estimate | Three-time estimate |
| Model | Deterministic Model | Probabilistic Model |
| Management of | Predictable activities | Unpredictable Activities |
| Suitable for | Non-research projects | Research and Development Project |
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method is a valuable tool for effective project management. It breaks down a project into specific tasks, providing clear focus during execution. This method helps allocate resources, such as funding, scheduling, and talent, ensuring timely completion of the project and high-quality deliverables.

































 Task Management
Task Management 


















 Customization
Customization
