Blog
Best practices in Enterprise Project Management
Is your project management falling behind as your organization grows? Many businesses encounter this challenge, with project demands outpacing their current capabilities, leading to overstretched resources and fragmented project information. This predicament forces leadership to choose: reduce project intake to match capabilities or evolve by implementing an Enterprise Project Management (EPM) system.
EPM suggests a holistic approach, integrating the entire organization into a cohesive system for managing projects. It emphasizes managing projects as interconnected efforts rather than isolated tasks, considering their collective impact on company goals and resource allocation.
This guide will show you how to identify if your organization is ready for EPM and navigate towards enhancing your project management approach effectively.
Understanding Enterprise Project Management
Enterprise Project Management (EPM) should not be confused with Project Portfolio Management (PPM), which adopts a top-down approach to manage project groups. EPM instead takes a bottom-up perspective, emphasizing the success of individual projects within the broader context of competing projects and resources. It stresses the importance of meticulous scheduling, planning, execution, and delivery, considering the collective impact on an organization’s goals.
EPM is defined as a methodology that aligns with an organization’s leadership vision, mission, strategy, goals, and objectives, facilitating a comprehensive view of the organization’s efforts. It’s a blend of mindset, communication, and action, supported by a system that organizes resources in line with the organization’s direction, offering a 360-degree perspective of all activities.
EPM requires a holistic management approach, integrating all project activities within the organization’s overall mission. A successful EPM strategy demands enterprise-wide commitment, inclusive processes, and a robust EPM platform to achieve a complete organizational overview. The aim is to formalize project management, incorporating a governance framework and best practices to efficiently manage multiple projects simultaneously.
Key Steps to Implementing an EPM Strategy Effectively
Adopting an EPM strategy is akin to guiding a teenager into adulthood, requiring education, tools, and maturity to navigate complex and unexpected project environments. For a smooth transition, organizations must carefully plan, analyze their current state, identify pain points such as visibility issues or resource limitations, and develop a phased plan to address these challenges.
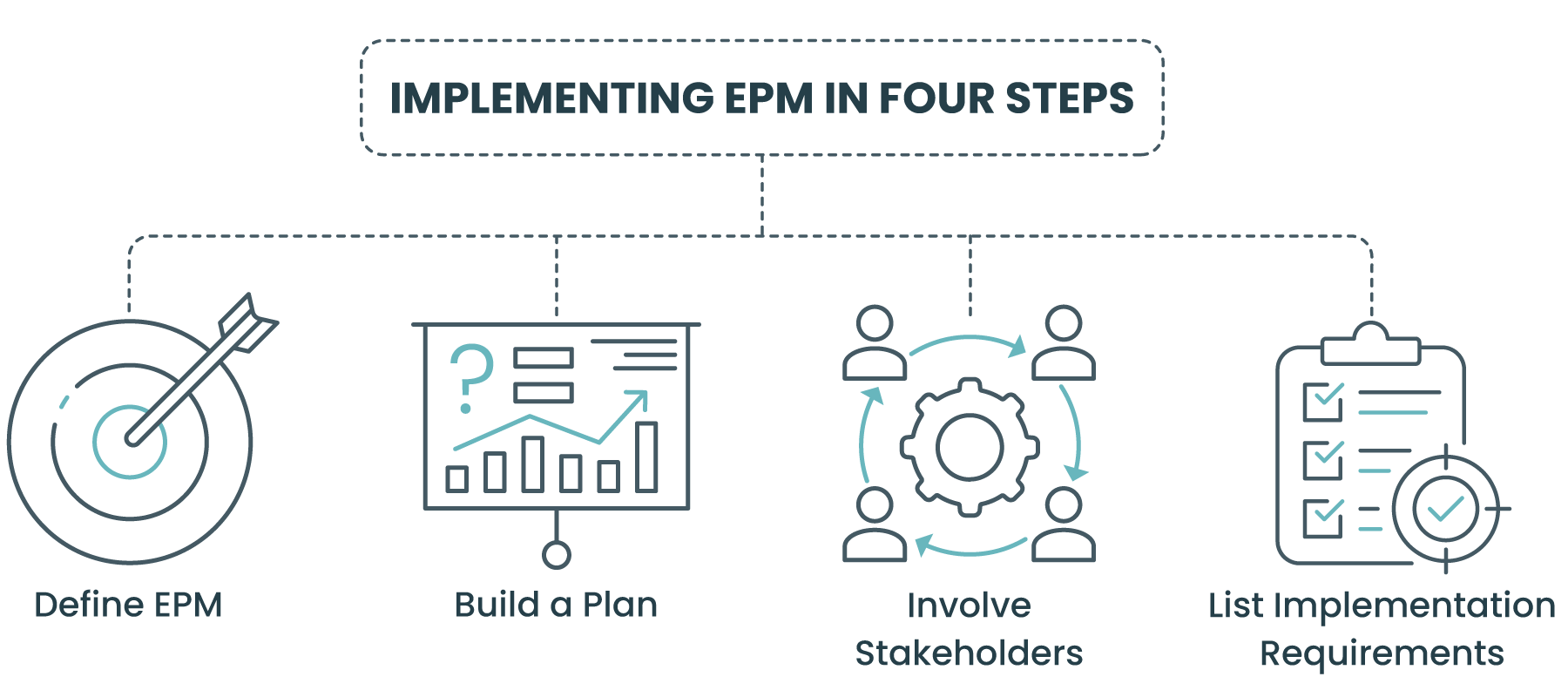
Implementing EPM in Four Steps:
- EPM Definition: Clearly define EPM’s purpose within your organization and develop a rollout strategy to align with stakeholders’ goals.
- Plan Building: With EPM defined, document a detailed plan outlining major tasks, creating a roadmap that covers people, processes, and technology.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Define roles and training for all stakeholders, ensuring clear communication and addressing any gaps that could hinder EPM adoption.
- Implementation Requirements Definition: List specific requirements and phases for organization-wide agreement, establishing clear expectations for the EPM strategy’s outcomes.
Proper planning and stakeholder involvement from start to finish can minimize the challenges of adopting an EPM strategy, setting the stage for successful implementation.
Assessing EPM Readiness in Your Organization
Many organizations recognize the need for Enterprise Project Management (EPM) too late, often when their ad-hoc project management processes can no longer keep pace with the demands of growth and customer expectations. Identifying the right time to shift towards a more structured EPM approach involves understanding both the challenges and the readiness of your organization to embrace a comprehensive EPM strategy. This involves more than just adopting new technology; it requires a fundamental shift in processes and organizational commitment.
EPM Readiness Checklist:

Growing Project Portfolio: If your projects are central to business success and your portfolio is growing, integrating an EPM strategy early can help manage this growth more effectively.
Resource Capacity Overwhelmed: When your project demands are about to surpass your resource capacity, it’s time to consider EPM. Planning your resource allocation in advance is key to avoiding bottlenecks.

Adherence to Best Practices: Incorporating industry best practices into your project management is a precursor to EPM readiness, fostering a culture that will support EPM adoptions.
Formal Processes and Governance: A formal governance framework provides the necessary structure for EPM, ensuring that the entire organization is aligned with its principles.
Tools and Technology Limitations: Recognizing when current tools are insufficient for effective project management is a clear sign that exploring EPM solutions could be beneficial.

Executive Support: The success of any EPM initiative hinges on executive buy-in for change management, essential for overcoming resistance and ensuring organization-wide adoption.
Understanding these factors can guide your organization towards a timely and successful EPM implementation, moving from ad-hoc processes to a strategic, holistic approach to project management.
Leveraging Technology and Tools for EPM Success
In the realm of Enterprise Project Management, the strategic selection and utilization of technology and tools play a pivotal role in enhancing project delivery and organizational efficiency. As projects become more complex and interconnected, leveraging the right set of tools can be the difference between success and struggle. This section explores best practices for selecting and implementing technology solutions that align with your EPM strategy, ensuring your organization not only keeps pace with current demands but is also future-proofed against upcoming challenges.
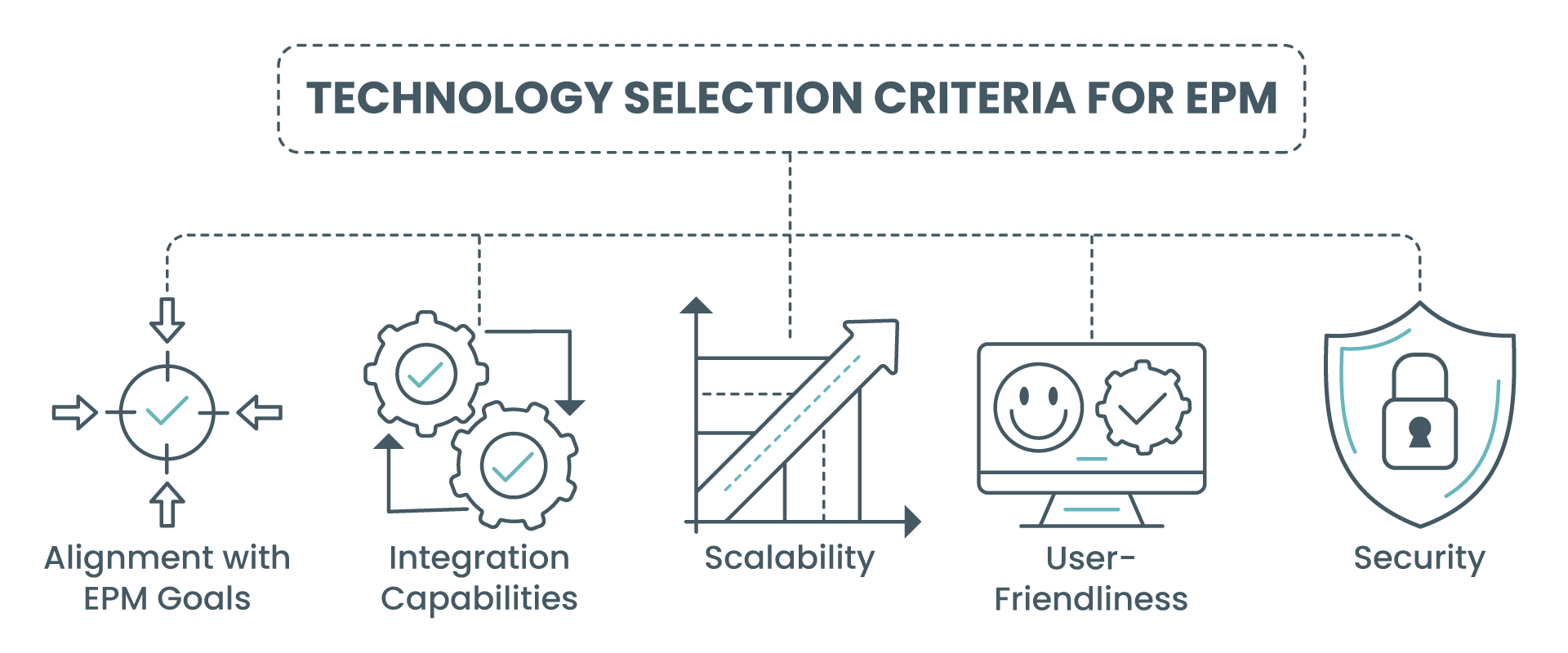
Technology Selection Criteria:
- Alignment with EPM Objectives: Choose tools that directly support your EPM goals, such as improving communication, enhancing visibility, or streamlining project workflows.
- Integration Capabilities: Opt for platforms that seamlessly integrate with existing systems and processes, minimizing disruption and maximizing cohesion across project management activities.
- Scalability: Ensure the tools can grow with your organization, accommodating an increasing number of projects and users without significant performance degradation.
- User-Friendliness: Select software that is intuitive and easy for all stakeholders to use, reducing the learning curve and encouraging widespread adoption.
- Security: Given the critical nature of project data, prioritize solutions with robust security features that protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
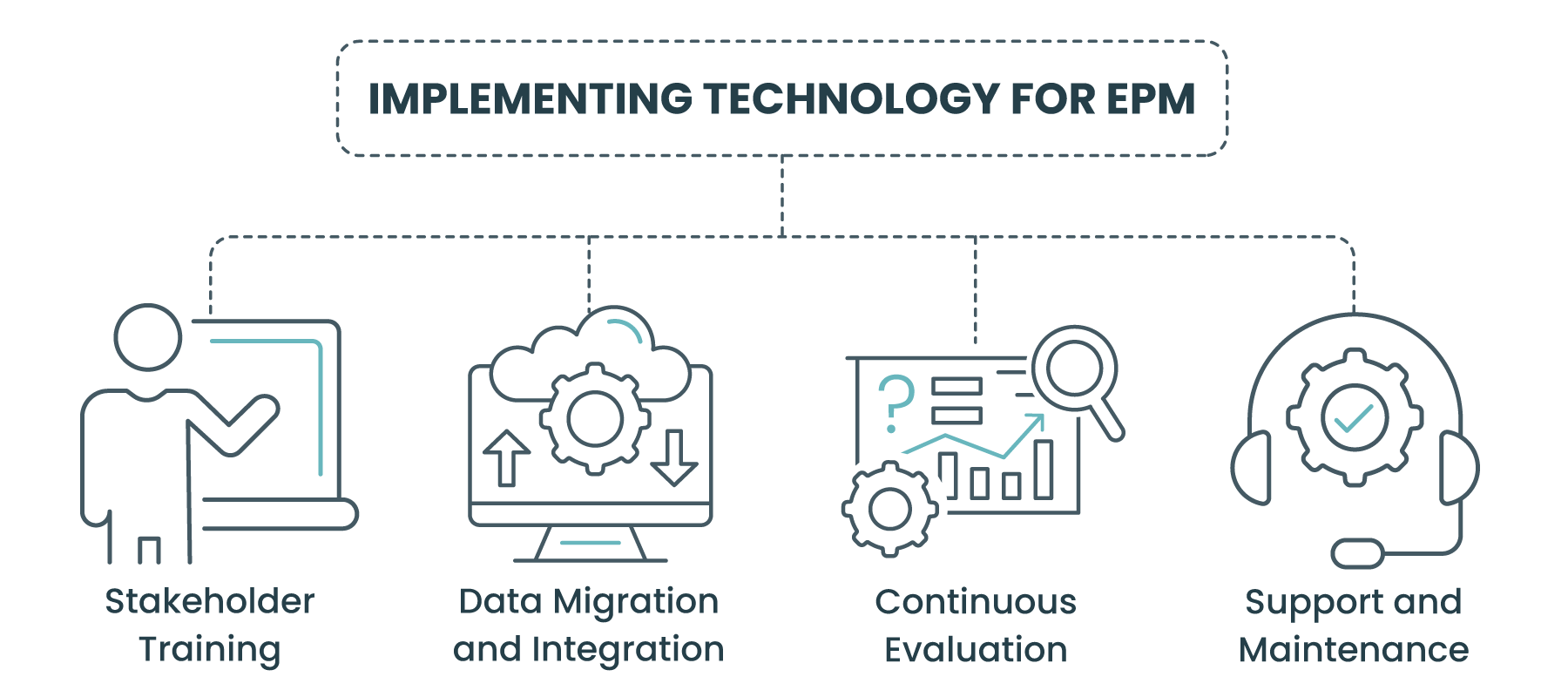
Implementing Technology for EPM:
- Stakeholder Training: Comprehensive training programs are essential for ensuring stakeholders can effectively utilize new tools, maximizing the investment in technology.
- Data Migration and Integration: Carefully plan the migration of existing project data into new systems and ensure smooth integration with other business tools to maintain data integrity and accessibility.
- Continuous Evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of implemented technologies, gathering feedback from users and making adjustments as necessary to optimize performance and usability.
- Support and Maintenance: Establish a clear plan for ongoing support and maintenance of EPM tools, including updates, troubleshooting, and user assistance to ensure long-term viability.
Incorporating technology and tools into your EPM strategy not only facilitates better project management practices but also empowers your organization to achieve a competitive edge. By carefully selecting and implementing the right solutions, you can enhance collaboration, improve decision-making, and ensure the successful delivery of projects aligned with your business objectives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adopting Enterprise Project Management is a transformative step for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of modern project landscapes. This journey, as outlined in our guide, involves strategic planning, leveraging technology, and fostering an inclusive culture that aligns with the organization’s broader goals. EPM is more than just a set of tools; it’s a fundamental shift towards a holistic approach to project management, necessitating commitment from every level of the organization. By prioritizing communication, stakeholder involvement, and continuous improvement, businesses can ensure their projects not only meet but exceed expectations, driving growth and innovation. Embrace this change with a mindset geared towards learning and adaptation, and your organization will be well on its way to achieving EPM excellence, where projects thrive and organizational objectives are achieved with precision and agility.

































 Task Management
Task Management 


















 Customization
Customization
