Blog
Stage-Gate Process vs. PMI Project Management: Key Differences and Applications
Introduction
In the world of project management, selecting the right methodology can significantly influence your project’s success. Two of the most widely recognized approaches are the PMI Project Management framework and the Stage-Gate Process. While both provide structured methods for managing projects, they cater to different types of initiatives and serve distinct purposes, particularly in product development. In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between PMI and Stage-Gate, helping you choose the right approach for your projects.
For a more in-depth visual explanation, check out our accompanying YouTube video.
Definition and Origins
What is PMI Project Management?
PMI Project Management, developed by the Project Management Institute (PMI), is a methodology based on the standards outlined in the PMBOK® Guide (Project Management Body of Knowledge). It offers a comprehensive framework for managing projects across a wide range of industries, emphasizing thorough planning, extensive documentation, and standardized processes. The framework is structured around ten key knowledge areas, ensuring all aspects of a project are covered from initiation to completion.
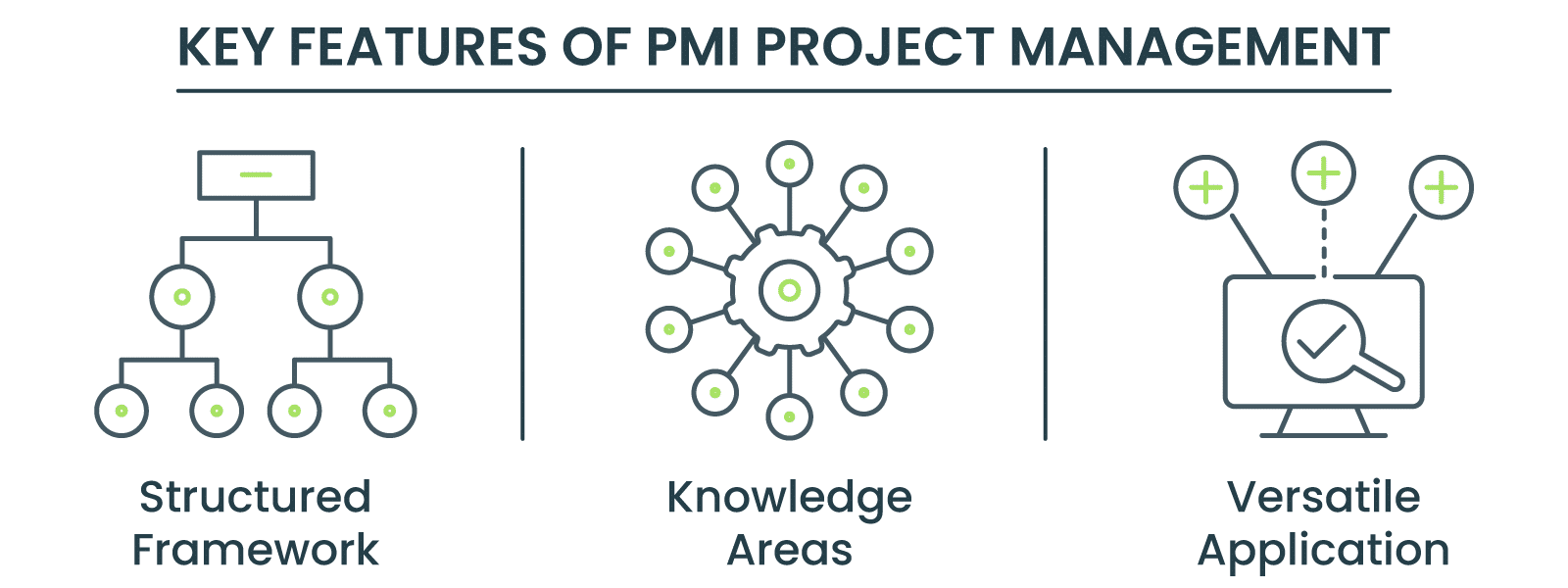
Key Features:
- Structured Framework: Provides detailed guidelines for every phase of a project, ensuring consistency and control.
- Knowledge Areas: Divides project management into ten distinct knowledge areas for thorough execution and management.
- Versatile Application: Widely applicable across various industries and project types, from IT to construction, making it a flexible tool for project managers.
What is the Stage-Gate Process?
The Stage-Gate Process, created by Dr. Robert G. Cooper, is a project management methodology specifically designed for product development. It divides the project lifecycle into distinct stages that are separated by “gates”—formal decision points where the project’s progress is evaluated based on predefined criteria. At each gate, decisions are made to either proceed, modify, or terminate the project, ensuring that risks are managed and resources are efficiently allocated.
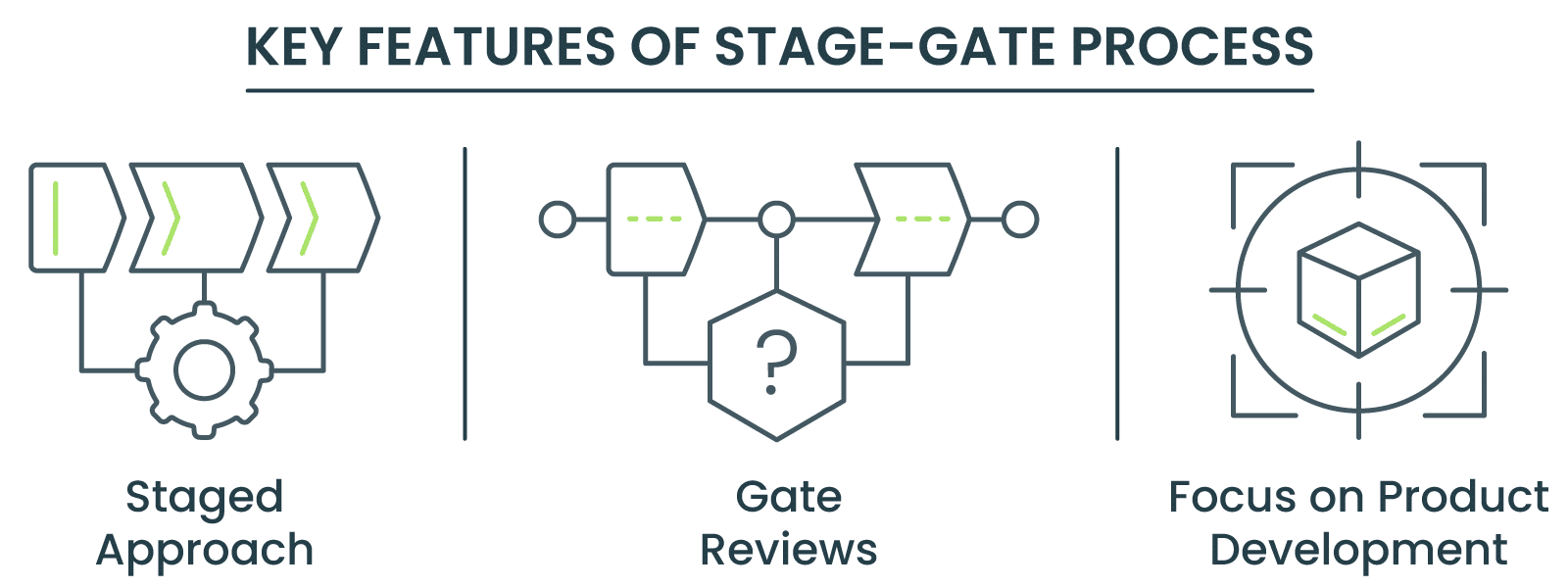
Key Features:
- Staged Approach: Projects are divided into phases, each with specific deliverables and objectives.
- Gate Reviews: At each gate, the project’s viability is assessed to ensure that it aligns with business objectives and market needs.
- Focus on Product Development: Widely used in industries like pharmaceuticals, software development, and consumer goods, where innovation and risk management are critical.
Differences Between PMI Project Management and Stage-Gate Methodology
Applicability
PMI Project Management: The PMI methodology is highly versatile and can be applied across a wide range of industries, including construction, IT, and services. It is ideal for projects that require structured, standardized processes, making it suitable for various project types, regardless of their complexity or industry.
Stage-Gate Process: The Stage-Gate process is primarily used in product development, particularly in R&D and manufacturing sectors. Its stage-based structure is tailored to innovation-driven projects, ensuring that each phase undergoes rigorous evaluation before progressing, making it well-suited for industries where iterative progress and frequent reviews are essential.

Structure
PMI Framework: The PMI methodology organizes projects into five distinct process groups:
- Initiating
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring & Controlling
- Closing
These process groups are supported by ten knowledge areas, which include Integration, Scope, Schedule, Cost, Quality, Resource, Communication, Risk, Procurement, and Stakeholder Management. This comprehensive structure ensures that all aspects of a project are thoroughly managed from planning through to delivery.
Stage-Gate Structure: The Stage-Gate process divides projects into the following stages:
- Discovery
- Scoping
- Business Case
- Development
- Testing & Validation
- Launch
After each stage, there is a “gate” where progress is evaluated based on predefined criteria. Only projects that meet the required standards at each gate proceed to the next stage, ensuring a controlled, selective progression that minimizes risk and optimizes resource allocation.
Flexibility
PMI Project Management: PMI emphasizes flexibility by allowing project managers to tailor processes to meet the specific needs of each project. While it provides a structured framework, it also supports adaptability, incorporating iterative methodologies like Agile to accommodate changing project requirements. This makes PMI suitable for a wide range of project types and industries that may require frequent adjustments.
Stage-Gate Process: The Stage-Gate process follows a more rigid progression through distinct stages, which can be less adaptable for projects requiring rapid changes. However, it does offer some level of customization at gates, where evaluations determine whether modifications are needed before moving forward. This ensures consistency in project progression while accommodating specific adjustments based on the evaluation results at each gate.
Decision-Making
PMI Project Management: In PMI, decision-making is informed by continuous monitoring and controlling throughout the entire project lifecycle. This ongoing oversight enables project managers to make real-time adjustments as needed, ensuring the project stays on track and aligns with its objectives. While PMI does not have formal “gates,” its emphasis on constant review provides flexibility in managing decisions at various stages.
Stage-Gate Process: The Stage-Gate process features formal decision points at the end of each stage, known as gates. At these checkpoints, stakeholders conduct rigorous evaluations based on predefined criteria to determine whether the project should proceed, be modified, or terminated. This structured approach provides a systematic method for managing risk, resources, and overall project viability.
Documentation Requirements
PMI Project Management: Extensive documentation is a hallmark of the PMI methodology. Detailed plans, reports, and records are required throughout all phases of the project. This approach ensures transparency and traceability for stakeholders, offering a comprehensive view of the project’s progress and facilitating informed decision-making at every stage.
Stage-Gate Process: While documentation is important in the Stage-Gate process, it is primarily focused on gate reviews. Instead of continuous, exhaustive documentation, the emphasis is placed on providing the necessary information for decision-makers to evaluate the project’s progress at key checkpoints. This approach minimizes administrative overhead while ensuring that critical decisions are well-informed.
Risk Management
PMI Project Management: Risk management is integrated throughout the entire PMI framework, from the project’s initiation to its completion. The methodology emphasizes the proactive identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks at every stage, ensuring that potential issues are addressed early and consistently monitored throughout the project lifecycle.
Stage-Gate Process: In the Stage-Gate process, risk management is a focal point at each gate. Before progressing to the next stage, risks are thoroughly assessed to ensure that any potential issues are identified and mitigated. This structured checkpoint system allows for continuous risk evaluation and ensures that only projects with manageable risks move forward.

Outcome Focus
PMI Project Management: The PMI methodology is designed to ensure that project deliverables meet stakeholder requirements and expectations. This is achieved through comprehensive planning, execution, and continuous monitoring and controlling processes. PMI’s focus on stakeholder engagement and quality control ensures that projects are aligned with predefined goals and deliver the expected outcomes.
Stage-Gate Process: The Stage-Gate process emphasizes ensuring that product development aligns with market demands and business objectives. Each stage is specifically designed to confirm that the project is viable, meets market needs, and supports long-term organizational goals. The process ensures that quality and strategic alignment are evaluated at every stage, facilitating informed decision-making at key points.

Conclusion: Which Methodology Is Right for You?
Both the PMI and Stage-Gate methodologies offer structured, proven frameworks for managing projects, but they are tailored to different types of initiatives.
- PMI is ideal for organizations that manage a diverse range of projects across various industries. Its flexibility, comprehensive documentation, and continuous monitoring make it suitable for complex projects that require adaptability and thorough stakeholder engagement.
- Stage-Gate, on the other hand, is specifically designed for product development and innovation-driven projects. Its stage-based structure and rigorous decision points ensure that only the most viable projects move forward, making it a strong choice for projects where managing risk and aligning with market needs are critical.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your project’s unique requirements. For innovation and product development, Stage-Gate offers a focused, stage-driven approach. For broader project needs across industries, PMI provides a versatile and comprehensive framework.
Explore More
To learn more about project management tools like Cerri Project that can streamline your workflows, visit our website.
* Stage-Gate® is a registered trademark of Robert G. Cooper.

































 Task Management
Task Management 


















 Customization
Customization
